Are you keen to explore the diverse array of sewing machines available? Sewing machines fall into two main categories: domestic machines for home sewing and industrial machines employed in factory settings and clothing manufacturing. While household sewing machines encompass six primary types, the industrial category features a multitude of specialized machines. This article endeavors to furnish you with comprehensive insights to assist you in choosing the optimal machine for your sewing endeavors.
Types Of Sewing Machines
Sewing machines, also referred to as cloth stitching machines, represent a pivotal invention that has reshaped the garment and upholstery industries. Selecting the appropriate sewing machine hinges on its functionalities and the anticipated workload. For sporadic sewing endeavors, a domestic sewing machine from a reputable brand should suffice. However, for daily and extended sewing projects, industrial machines are better suited, each serving a unique function.
Domestic Sewing Machines
Domestic sewing machines, designed for household use, are the top pick for home sewers. While these standard models may vary in quality and durability, they’re generally not built for continuous daily usage. Lightweight and portable, they offer versatility with a range of stitches and features.
Industrial Sewing Machines
Industrial sewing machines are engineered to be durable and versatile, capable of handling a wide range of fabrics, from heavy-duty upholstery materials to leather, rubber, plastic, and canvas. These machines are essential in industrial settings, where they excel in various projects involving tough materials. Some industrial machines have even found their way into home industries, thanks to their robustness and reliability. There are several types of industrial sewing machines, each specializing in a specific function, unlike domestic machines that offer multifunctionality. Constructed with sturdy metal bodies and interiors and featuring mechanical components with minimal or no computerized parts, industrial machines are built to withstand prolonged use. Many industrial models feature a flatbed design, with the sewing area recessed into the table for added stability.
Due to their specialized design, industrial sewing machines tend to come with a higher price tag compared to domestic counterparts. However, they often hold their value well, making the second-hand market a viable option for buyers. Brands like Juki and Singer are well-known for producing high-quality industrial sewing machines.
When considering an industrial sewing machine, it’s important to recognize that they require a bit more skill to operate, similar to driving a truck compared to a car. However, once you’ve mastered the machine, you’ll appreciate its capabilities. Personally, I’ve owned both an industrial straight stitch machine and an industrial leather machine.
One notable characteristic of industrial sewing machines is their noise level; they tend to be louder and operate at higher speeds. Achieving precise control over the foot pedal speed is crucial. Many industrial machines need to be inset or bolted to a table, with a connection to the foot pedal, to minimize vibrations during operation.
Electronic Sewing Machine
Electronic sewing machines provide a wide range of features and the ease of electronic operation. Available in various brands, each offering unique stitch options and lengths, these machines usually consist of an upper thread and a bobbin thread underneath. Unlike computerized models, electronic sewing machines are controlled using knobs instead of electrical panels. They typically offer straight stitches, zigzag stitches, and some decorative stitches, with certain models even featuring a buttonhole function. Furthermore, heavy-duty sewing machines like the Singer model highlighted below are engineered specifically for sewing thicker fabrics.

Compact and Portable Sewing Machines
Electronic machines also include mini portable models, which, although convenient for their portability, lack the robustness needed for extensive sewing tasks. These mini machines are ideal for small projects and mending due to their lightweight design. However, they may not have the power required for larger projects or extended sewing sessions.
Computerized or Automated Sewing Machines
Moving up the ladder of sewing machines, computerized and fully automated models showcase a plethora of functions and features. With LCD screen displays, automatic needle threading, and thread cutters, these machines also boast embroidery stitches, adjustable tension controls, and stitch lengths. They effortlessly produce buttonholes and come equipped with built-in stitch programs.
Although these machines may be pricier, they are crafted to be robust and enduring. Reputable manufacturers often offer lessons and warranties for these premium-grade machines.
Embroidery Machines
Investing in an embroidery machine is a must if you plan on delving into embroidery frequently. These machines usually come loaded with built-in designs and memory functions for storing patterns. With a USB port, embroiderers can conveniently access and import additional designs into the machine’s memory. However, it’s important to recognize that embroidery machines typically belong to the higher price range, with some models fetching several thousand dollars.

Serger Or Overlocking Sewing Machine
The serger, also known as the overlock machine, has quickly become a staple in the sewing machine lineup, especially for sewing stretch knits and fleece, particularly in active sportswear. With options for three or four threads and equipped with a thread cutter, the overlocker excels at sewing, trimming, and oversewing the edges of seams, resulting in a clean and professional finish.
Additionally, the serger’s versatility extends to creating delicate gathers, further enhancing its utility. However, threading a serger can be tricky, so if your budget allows, opting for a self-threading model can save you time and frustration.
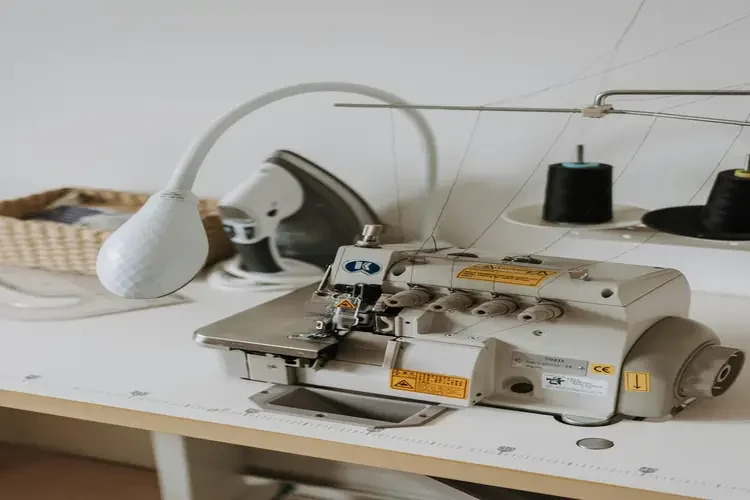
Cover Stitch Machine
This particular industrial machine is adept at executing various tasks including hemming, binding, topstitching, and incorporating decorative elements.
Lock Stitch Machine
Lockstitch sewing machines create stitches resembling backstitches, resulting in an even appearance on both sides of the fabric. These machines can perform straight stitches and zigzag stitches with ease.

Chain Stitch Machine
Produces a chain stitch that’s beneficial for stretch fabrics and for creating binding and decorative effects.
Blind Stitch Machine
This apparatus excels in crafting concealed hemstitches, delivering swift and efficient outcomes, particularly ideal for sewing hems on knit fabric.
Button Sewing Machine
In the realm of sewing machines, there are specialized versions tailored for sewing buttons. These machines come with distinctive holders or clamps designed to securely grip the button while it’s being sewn. They boast adjustable settings for stitch width and button spacing, accommodating buttons of different sizes and styles. While industrial sewing machines are primarily dedicated to this task, it’s worth noting that you can also sew buttons using a standard home sewing machine.
Zig-Zag Machines
This industrial sewing machine specializes in zigzag stitching and is primarily used in the production of bras and underwear to attach elastic. Built for heavy-duty performance, these industrial-grade machines are designed to endure continuous use. Beyond their primary function, zigzag machines can also be employed for decorative embroidery, appliques, and joining fabrics edge to edge.
Back Tack Machines
These diverse sewing machines are designed specifically for crafting the intricate stitches typically found along the top edges of pockets, belt loops, and other areas that necessitate extra reinforcement.
Flat Bed Sewing Machines
Flatbed sewing machines are equipped with a level surface where the fabric sits during stitching. While frequently utilized in industrial environments, domestic variants are also accessible. This flat foundation offers robust support for sewing larger items.
Cylinder Bed Sewing Machines
A cylinder bed sewing machine is specially designed for stitching small, rounded items such as cuffs and shoes. Its cylindrical shape allows for smoother sewing of tubular items and provides easy access to hard-to-reach areas within an item.
Buttonhole Sewing Machines
Industrial buttonhole sewing machines are designed specifically to automate the process of sewing buttonholes in garments and various other items like cushions. These machines play a vital role in enhancing efficiency within the garment industry, ensuring the production of high-quality, seamless, and perfectly symmetrical buttonholes. Featuring adjustable settings, users can tailor the buttonhole length, width, and shape to their specific requirements, and achieve a precise cut for a refined finish.
Safety Stitch Sewing Machine
A safety stitch combines features of both a two-thread Chainstitch and a three-thread Overlock Stitch. This specialized machine is engineered to tidy up edges and stitch seams concurrently. While it’s commonly paired with an overlock sewing machine, you can also find standalone safety stitch machines.
You may also like:
- The History Of Sewing Machine
- Sewing Machine Parts And Functions
- Using a Seam Ripper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Sewing Kits: A Comprehensive Guide
- Count of Yarn: Explanation and Varieties
- Yarn Manufacturing Process
- Varieties of Woven Fabrics and Their Applications
- Non Woven Geotextile Fabric
- What is Sisal Fiber? Properties, Structure, and How It Made?
Share this Article!

