What is fabric?
Fabric is crafted from solutions, fibers, yarns, or textiles. Non-woven fabrics and felts stem directly from fiber webs, yet they possess restrictions in their utility. The most effective method of crafting textile fabrics for various intents involves the mechanical transformation of yarn into fabric. This process encompasses weaving, knitting, or other traditional techniques.
Types of Fabric
Four main methods are used to manipulate yarn into fabric
- Interweaving
- Interloping
- Intertwining
- Nonwoven
These techniques have evolved from manual labor on simple frames to advanced manufacturing processes conducted by automated machinery.
What is Interweaving Fabric?
Weaving occurs when two sets of straight threads, known as warp and weft, intersect and intertwine, forming right angles. This method represents the oldest and most widespread technique for crafting lengthy fabric pieces with straight edges.
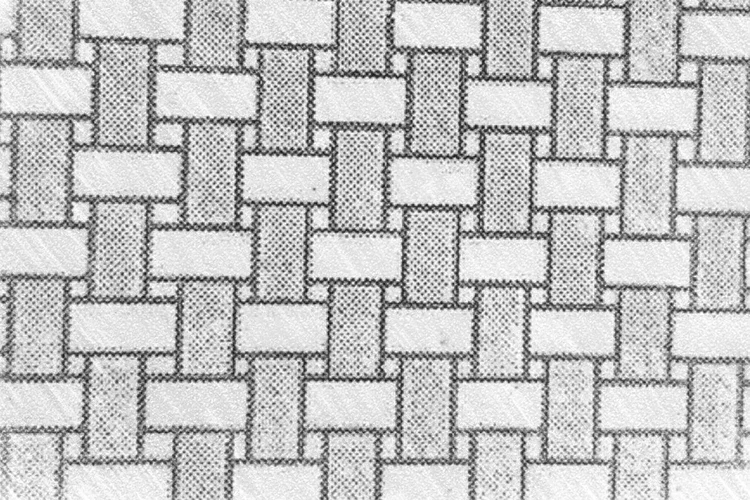

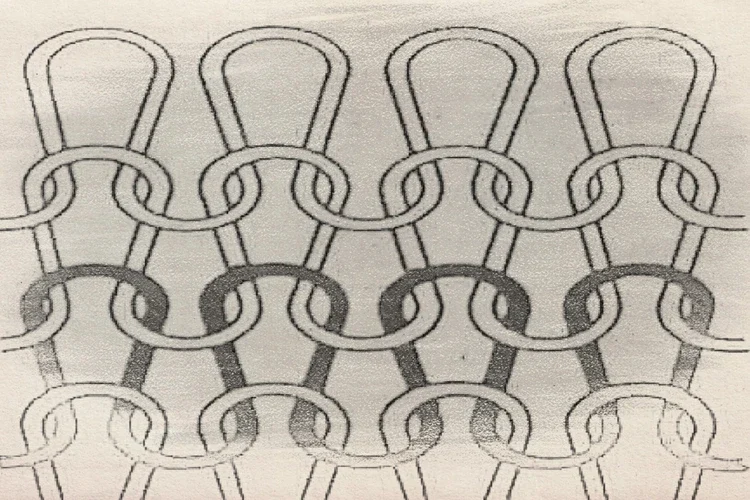
What is Interloping Fabric?
Knitting crafts loops with yarn, letting go of each loop after it intertwines with the next, resulting in a sturdy structure. Yarn passing between loops enhances their cohesion. It ranks as the second most favored technique, following weaving, for crafting textiles. Annually, the global production exceeds seven million tons of knitted goods. Knitting has been a centuries-old practice for shaping snug-fitting items, and modern advancements have expanded its applications in clothing, household items, and industry, whether in shaped or unshaped forms.
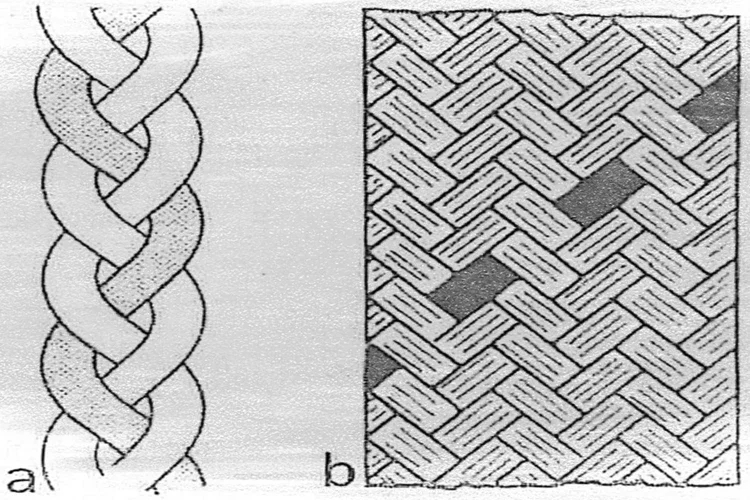
What is Intertwining Fabric?
This involves a range of methods like braiding and knotting, where threads weave together at different angles. These techniques frequently result in distinctive structures tailored for specific, restricted uses.
What is Nonwoven Fabric?
This rising field within the textile industry has seen substantial growth since World War II, driven by higher production rates and cost-effectiveness. Nonwovens are adaptable, porous substances made up of one or multiple layers of fibers. These fibers can be arranged in a particular direction or randomly distributed. They are subsequently bonded together using chemical, thermal, or mechanical techniques to produce textile items. Nonwovens predominantly feature flat compositions.
Short Note
| NAME | MANUFACTURING PROCESS |
| WOVEN FABRIC | WEAVING (INTERLACING OR INTERLACEMENT) |
| KNIT FABRIC | INTERMESHING OR INTERLOOPING |
| BRAID FABRIC | INTERTWINING |
| NONWOVEN FABRIC | CHEMICAL, THERMAL, OR MECHANICAL TECHNIQUES |
You may also like:
- Count of Yarn: Explanation and Varieties
- Yarn Manufacturing Process
- What is Hemp Fiber? Properties, Advantages and Disadvantages.
- What is Ramie Fiber? Properties, Advantages and Disadvantages.
- What is Sisal Fiber? Properties, Structure, and How It Made?
- Pina Fiber: History, Properties, Production Process
- Coir Fiber: Properties, Production Process and Advantages
- Rayon Fiber: History, Properties, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Acrylic Fiber: History, Properties, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Nylon Fiber: Properties, Advantages and Disadvantages
Share this Article!

